In the complex world of cannabinoids, distinguishing between the numerous compounds derived from the cannabis plant can be both fascinating and confusing. Two such compounds, THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and Delta 9 THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), are often discussed in similar contexts. While they share a chemical lineage, they differ significantly in structure, effects, and how they interact with the human body. By breaking down the science and functionality of these two compounds, we’ll explore their unique roles, properties, and potential uses.
What is THCA?
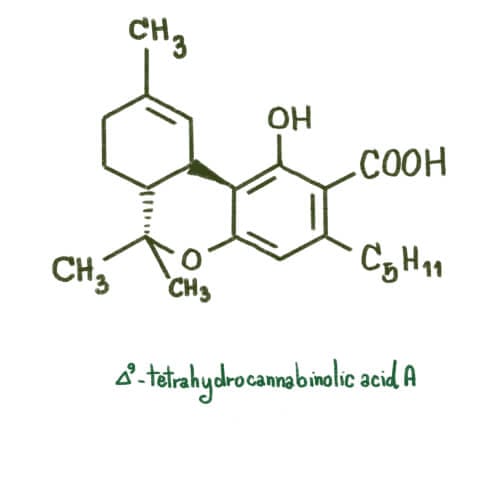
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in raw cannabis plants. It’s often considered a precursor to Delta 9 THC because, under specific conditions such as heat, THCA converts into Delta 9—a process called decarboxylation.
THCA’s Role in the Cannabis Plant
THCA is one of the most abundant cannabinoids in freshly harvested cannabis flowers. It is produced in the trichomes, the tiny resinous glands that coat the plant’s surface. THCA doesn’t produce intoxicating effects because it cannot efficiently bind to CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system. These receptors are largely responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis.
Properties of THCA
While research is still ongoing, THCA has been observed to have potential for specific uses due to its non-intoxicating nature. However, any purported benefits are still subject to clinical research and should not be taken as established facts.
What is Delta 9 THC?
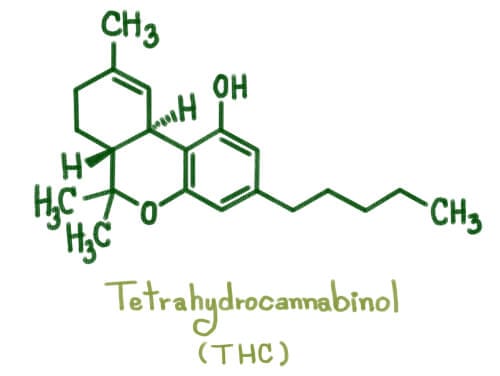
Delta 9 THC is the most well-known cannabinoid responsible for cannabis’ psychoactive effects. It is the compound that produces the “high” associated with cannabis use. Delta 9 THC directly binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, producing a range of effects depending on the dose, strain, and individual tolerance.
How Delta 9 is Formed
Delta 9 does not naturally exist in significant quantities in raw cannabis. Instead, it is formed when THCA undergoes decarboxylation. This process involves exposing THCA to heat or light, which removes a carboxyl group (COOH) from the molecule. This chemical transformation changes the structure of THCA into Delta 9, making it psychoactive.
Properties of Delta 9
Delta 9 THC is known for its wide-ranging effects. Some people seek it out for recreational enjoyment, while others use it for therapeutic purposes. Despite its widespread use, it’s essential to note that individual reactions to Delta-9 THC can vary.
The Key Differences Between THCA and Delta 9 THC
While both compounds are chemically related, they differ in their chemical structure, psychoactive effects, and methods of consumption. Let’s explore these differences in greater detail, shall we.
Difference #1: Chemical Structure
THCA and Delta 9 THC have nearly identical molecular structures, but the presence of a carboxyl group (COOH) on THCA makes a significant difference. This carboxyl group is what prevents THCA from binding effectively to CB1 receptors, rendering it non-intoxicating. Delta 9, on the other hand, lacks this carboxyl group, allowing it to bind to CB1 receptors and produce its characteristic psychoactive effects.
Difference #2: Psychoactive Effects
THCA is non-intoxicating, meaning it does not cause the “high” commonly associated with cannabis. Delta 9, however, is highly psychoactive and is the primary reason for cannabis’ recreational use. The difference in psychoactivity stems from how the two compounds interact with the brain’s endocannabinoid system. THCA cannot activate CB1 receptors effectively, while Delta-9 THC binds to them directly, causing various effects.
Difference #3: Activation Through Decarboxylation
THCA and Delta 9 are also differentiated by how they are consumed. THCA must undergo decarboxylation to convert into Delta 9. This transformation occurs when cannabis is smoked, vaped, or cooked into edibles. Without heat or light exposure, raw cannabis with high THCA content will not produce significant psychoactive effects.
Difference #4: Consumption Methods
THCA is typically consumed in its raw form, aka flower and pre-rolls. You can also experience THCA in an edible, capsule, or tincture form. For Delta 9, it’s consumed in various ways too, including smoking, vaping, and dabbing, as well as being infused into edibles and tinctures. For vaping, smoking, and dabbing in particular, this generally involves some form of heat to activate the psychoactive properties of Delta-9 THC.
How THCA and Delta-9 THC Interact with the Endocannabinoid System
The human body contains an intricate network called the “endocannabinoid system (ECS)”, which has a critical role in regulating functions such as mood, appetite, and sleep. Cannabinoids like THCA and Delta 9 THC interact with this system in distinct ways.
THCA’s Interaction with the ECS
THCA interacts with the ECS differently than Delta 9. It does not effectively bind to CB1 receptors but may influence other receptors or pathways. However, the extent and significance of THCA’s interaction with the ECS remain subjects of ongoing study.
Delta 9’s Interaction with the ECS
Delta 9 primarily interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain and CB2 receptors in the immune system. This interaction leads to the psychoactive effects of Delta-9 THC and its broader range of potential effects.
THCA vs. Delta 9 THC: Legal Status
The legal status of THCA and Delta 9 THC can vary significantly depending on jurisdiction.
THCA’s Legal Status
THCA is often classified differently from Delta 9 because it is non-intoxicating in its raw form. In some areas, products containing THCA may be legal if they do not contain decarboxylated THC or exceed certain THC thresholds. However, it’s important to note that once THCA is decarboxylated, it becomes Delta 9, which can lead to legal complications.
Delta 9’s Legal Status
Delta 9 is subject to more stringent regulations due to its psychoactive properties. Here in the United States for example, Delta 9 derived from hemp is federally legal if it contains no more than 0.3% Delta-9 THC on a dry weight basis. Cannabis-derived THC remains illegal at the federal level but is legal in various states. Still, consumers should be aware of their local laws when purchasing or using products containing THCA or Delta 9.
Should You Choose THCA or Delta 9 THC?
The decision between THCA and Delta 9 THC depends on individual preferences and needs. Consider the following factors:
- Psychoactivity: If you prefer a non-intoxicating experience, THCA is the better choice. For those seeking psychoactive effects, Delta 9 THC is the clear option.
- Consumption Methods: Raw cannabis products preserve THCA, while heat-activated methods release Delta 9 THC.
- Legal Restrictions: Always check the legal status of THCA and Delta 9 THC in your area before making a purchase.
Bottom Line: THCA and Delta 9 THC Are Not the Same
While THCA and Delta 9 THC share a chemical relationship, they are fundamentally different in structure, effects, and applications. THCA is the non-intoxicating precursor to Delta 9 THC, which is psychoactive and responsible for the “high” associated with cannabis. And so, understanding these differences is essential for anyone exploring cannabis products, whether for recreational or therapeutic purposes. By distinguishing between THCA and Delta 9 THC, you can make informed decisions about which cannabinoid aligns best with your needs and preferences.
Please Note: This information is only valid as per December 11th, 2024.